
We recommend that when using two suture buttons, one should be directed anteriorly and the second in a transmalleolar direction. The increased stability of the syndesmosis from two anteriorly directed Tightropes may have predisposed to nonunion. This is the first reported case of a Maisonneuve fracture treated by syndesmosis suture button stabilisation resulting in fibula nonunion. Spiral fracture of the proximal fibula with or without fracture of the medial. By 3 months following fixation he reported alleviation of pain and improving ankle function. At 9 months following the initial injury, the fracture was surgically debrided and stabilised using a locking compression plate, and synthetic bone graft applied. Plain radiographs and CT scan revealed a fibula nonunion. This type of injury can be difficult to detect. It is caused by a pronation-external rotation mechanism. There is an associated fracture of the medial malleolus or rupture of the deep deltoid ligament of the ankle. Maisonneuve fracture refers to a combination of a fracture of the proximal fibula together with an unstable ankle injury (widening of the ankle mortise on x-ray), often comprising ligamentous injury (distal tibiofibular syndesmosis, deltoid ligament) and/or fracture of the medial malleolus. At 6-month follow-up he had significant pain around the mid-calf, and also ankle pain and stiffness. The Maisonneuve fracture is a spiral fracture of the proximal third of the fibula associated with a tear of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis and the interosseous membrane. Maisonneuve fractures comprise a fracture of the proximal fibula associated with fracture or ligament injury of the. The syndesmosis was reduced and stabilized using two anteriorly directed suture button Tightropes. Left untreated, the result can be long-term ankle instability and early-onset arthritis. Plain radiograph at 3 months following internal fixation of the fibula revealing healing of the fracture.Ī 26 years old male sustained a Maisonneuve fracture with diastasis of the syndesmosis. A Maisonneuve fracture is a complex ankle and leg injury. The fracture was then stabilized using a 7-hole locking compression plate (Synthes, Solothurn, Switzerland) and synthetic Stimulan bone graft (Biocomposites, Keele, UK) was applied.īy 3 months following fixation the patient reported complete alleviation of pain in the calf and improving function to the ankle (AOFAS = 91) and radiographs confirmed union.
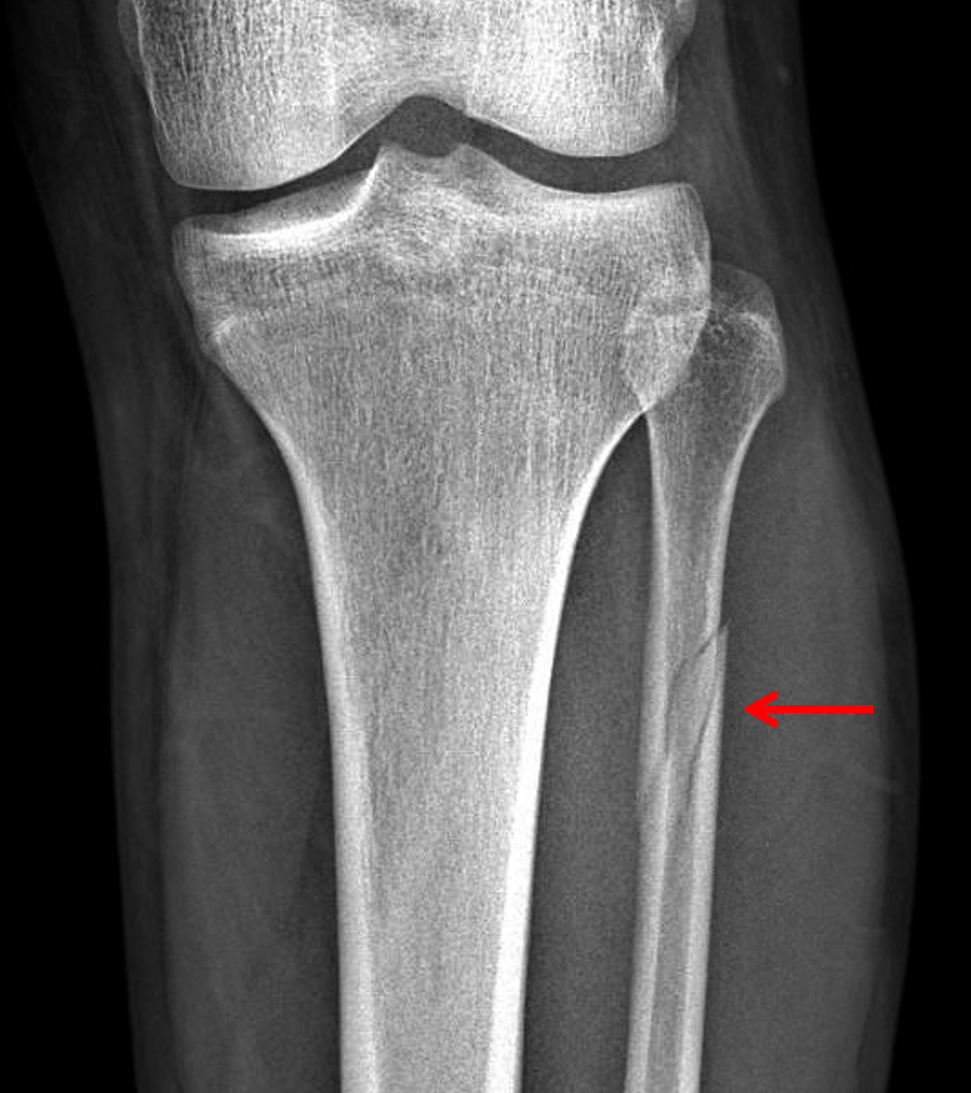
Fibrous tissue was removed from the fracture site with drilling of sclerotic bone.

Intra-operative photograph after debridement of the nonunion site including drilling of the sclerotic bone ends.Īt 9 months following injury, the fibula nonunion was explored. Plain radiograph showing the unstable syndesmosis was stabilised using two anteriorly directed Tightropes.ĬT images confirming the fibula nonunion and sclerosis of the bone ends.Īxial MRI revealing the reduced syndesmosis and healing of the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (AITFL). This article reports the case of a 34-year-old male. commonly achieved by trans-syndesmotic screws. Alternative stabilization mechanisms exist (e.g.Anterior Impingement- After Total Ankle Replacement One of its variants includes a proximal tibiofibular dislocation, which is an even more unusual injury.internal fixation of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis 6.Treatment and prognosisĪlthough management is variable depending on the complexity of injuries, this type of fracture pattern is generally managed by operative treatment.
#MAISONNEUVE FRACTURE PLUS#
The Maisonneuve fracture is defined by the above findings plus a proximal fibular fracture (high Weber C), usually in the proximal third 7. When these ankle injury types are seen without a fracture of the lateral malleolus, further imaging of the entire fibula is recommended. A spiral fracture of the proximal third of the fibula near the head accompanied by tearing of the interosseous membrane and distal.
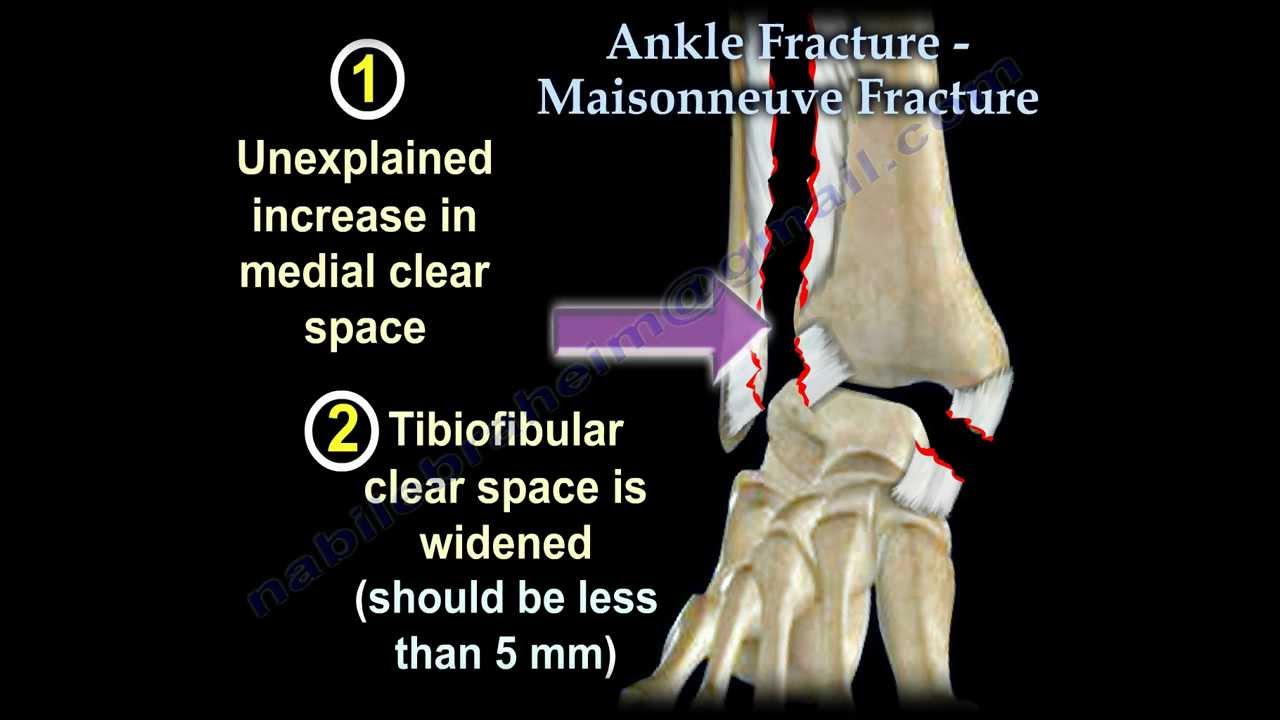
Admit patients with open fractures or neurovascular compromise. Should reduce and place in a short leg splint, non-weight bearing, immediate orthopedic consult to be seen while in ED. If untreated the instability can lead to chronic pain and long-term disability. Ankle views may show a fracture of the medial malleolus or widening of the medial ankle joint space due to deltoid ligament injury, as well as widening of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis. Maisonneuve fractures are associated with ankle instability, require surgery.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
